1. Two Sum
Array
Hash Table
Description
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of
the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example
Input : nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output : [0,1]
Explanation :
Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
Intuition
- In this question we find out two different indices it's value sum is given
targetvalue nums[i] + nums[j] = targetherei != j
Approaches
Brute Force
- One brute force approach is to consider every pair of elements and check if their sum equals the target.
- We need to find out
two different indicesthat sum istarget valueso we take one by oneith indices and one by onejth indices and check it's sum is equal totargetvalue. - We take two for loops one is for traveling
iindices and second one is travelingjindices.
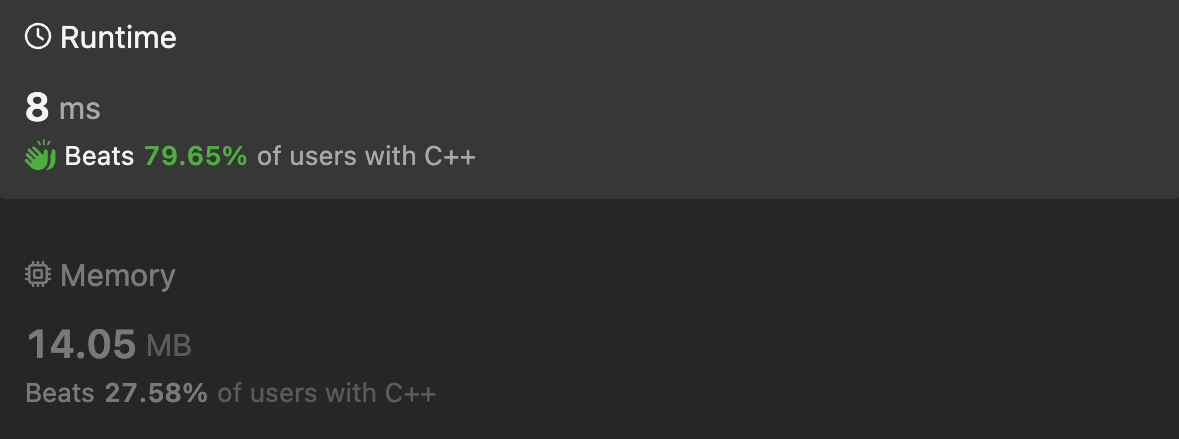
Time Complexity
O(N * N)where 'N' is nums length
Space Complexity
O(1)
Code
two-sum.cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target)
return {i, j};
}
}
return {}; // solution not found
}
};Analysis
Using Hash Table
- We have this equation
nums[i] + nums[j] = target nums[j] = target - nums[i]- In one pass we have
targetandnums[i]so using above formula and hash table we findnums[j]. - Each iterator we store index value and index at hash table
table[nums[i]] = i - At each index we check
table[target - nums[i]]is present if present then we return{i, table[target - nums[i]]}
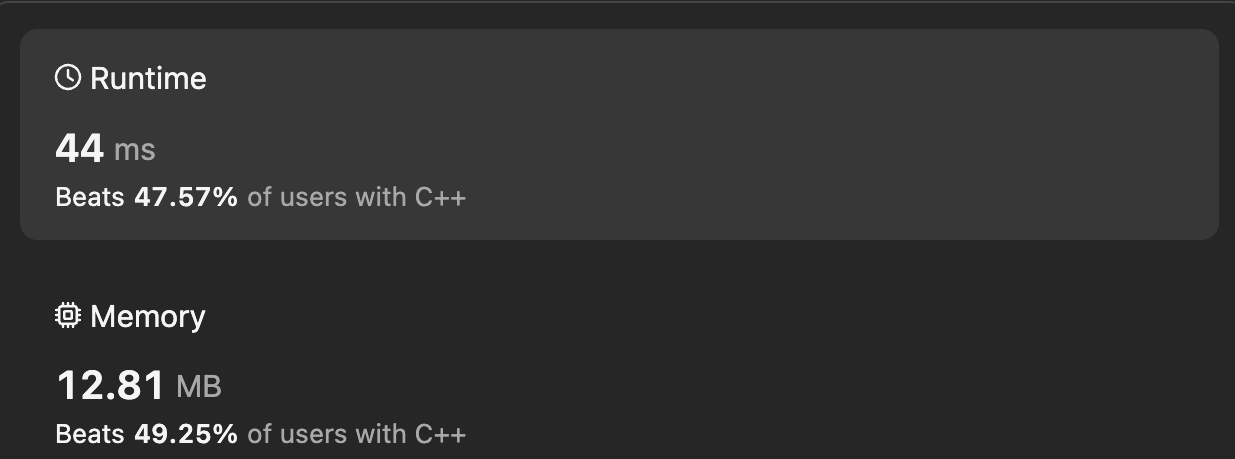
Time Complexity
O(N)where 'N' is nums length
Space Complexity
O(N)
Code
two-sum.cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
unordered_map<int, int> table;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(table.find(target - nums[i]) != table.end())
return {i, table[target - nums[i]]};
table[nums[i]] = i;
}
return {}; // solution not found
}
};Analysis